Asymmetric risk, a concept deeply ingrained in the world of finance, refers to a situation where the potential for gains and losses is not proportionate.
In other words, the risk-reward profile is skewed, offering the possibility of significant rewards compared to relatively limited downside.
This article explores the nuances of asymmetric risk, its implications for investors, and how understanding this concept can lead to more informed decision-making in financial endeavors.
Índice
The Nature of Asymmetric Risk
Traditional investment models often assume symmetric risk, where potential gains and losses are expected to be relatively equal.
Asymmetric risk challenges this notion by acknowledging that not all risks are created equal. In asymmetric risk scenarios, investors seek opportunities where the potential upside far outweighs the potential downside. This creates a favorable risk-reward ratio, providing a cushion against losses while allowing for substantial gains.

How Investors can utilize Asymmetric Risk
Professional investors often encounter situations with asymmetric risk. Recognizing and capitalizing on these opportunities can be highly profitable.
By strategically identifying investments with favorable risk-reward profiles, investors can enhance their portfolio’s overall performance.
Asymmetric risk allows for the pursuit of high-reward opportunities while managing exposure to potential losses, aligning with the principle of maximizing gains while minimizing downside risk.

Examples of Asymmetric Risk
One common example of asymmetric risk is found in options trading. Options provide investors with the ability to control a large position with a relatively small upfront investment.
While the maximum loss is limited to the initial investment, the potential gains can be substantial if the market moves favorably. This illustrates the asymmetry inherent in certain investment strategies.
Bitcoin the Asymmetric Bet
Bitcoin can be a good idea even if there’s a high chance of failure because it’s an “asymmetric bet” with potentially high returns compared to the risk. This means even if Bitcoin only has a small chance of succeeding, the potential payoff is so much bigger than the potential loss that it’s worth considering as an investment.
According to Seeking Alpha author John Rhodes, Bitcoin has a big upside with a small chance of total failure.
“Looking out to 2030, each Bitcoin is potentially worth $10,000,000. Looking out to 2035, and beyond, and each Bitcoin is potentially worth $100,000,000.” Source Seeking Alpha
He brings up a simple table, visualizing the asymmetric opportunity Bitcoin represents:
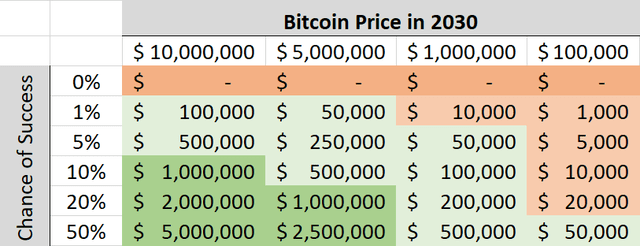
The table shows the 4 different scenarios for Bitcoin’s price in 2030 in the first line. On the left side we can see how likely, or unlikely it is that Bitcoin survives. Green means better outcomes and red indicates weaker outcomes, or even complete failure.
Why is Bitcoin an asymmetric risk? Bitcoin has a fixed supply (21 million), unlike fiat currencies which can be inflated by governments. Institutional investors like Fidelity, Blackrock and VanEck and expert traders like Greg Foss are taking Bitcoin seriously and see it as a potential store of value.
Even if Bitcoin fails completely, the expected value (considering both chance of success and potential returns) can still be positive. Bitcoin doesn’t have to be an all-or-nothing decision. A small allocation can be a good way to solve the inflation problem of fiat currency and other portfolio risks.
Professional investors have to start thinking in terms of probabilities and expected value when considering Bitcoin as an investment. For savers, it’s a much easier choice as Bitcoin is a superior store of value compared to all other options.
Conclusión
Understanding asymmetric risk is a key element of strategic decision-making. Investors who can identify and capitalize on opportunities with favorable risk-reward ratios position themselves for success. By recognizing that not all risks are equal and embracing the concept of asymmetric risk, individuals can navigate the complexities of the market with a more informed and calculated approach, ultimately optimizing their chances for financial success.









