Bitcoin’s value can be compared to that of precious metals, according to some. Both have specific uses and are in limited supply. Gold and other precious metals are utilized in industrial applications, but the blockchain, the technology that underpins bitcoin, has some uses in the financial services sector. Due to its digital heritage, bitcoin’s value may increase to a level where it may someday be used as a medium for retail transactions.
Inhaltsübersicht
The Value of Traditional Currencies
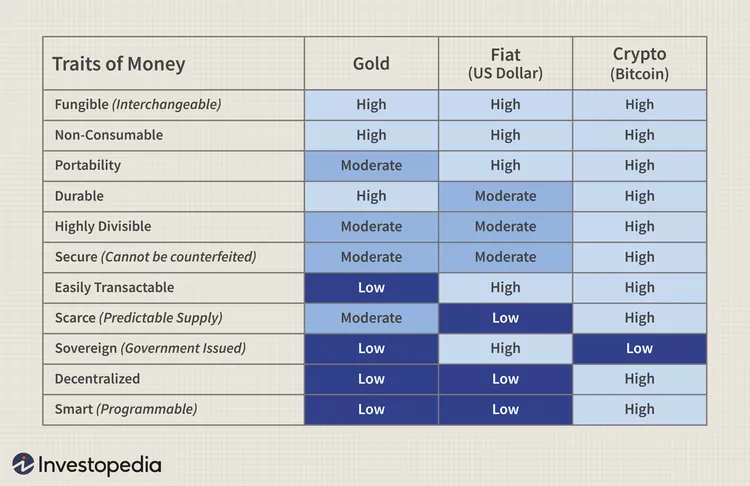
A good currency must have six essential qualities in order to be effective: uniformity (resistance to counterfeiting), acceptance, mobility, acceptability, and scarcity. These characteristics enable a currency to be widely used in an economy. They also ensure that the currencies are secure and safe to use while limiting monetary inflation.
If a currency serves as a store of value, or, to put it another way, if it can consistently hold its relative value over time, then it is useful. Because commodities and precious metals were seen to have a fairly steady value throughout history, many communities have utilized them as a form of payment.
Societies ultimately adopted minted currency as a substitute for the bulky amounts of cocoa beans, gold, or other early types of money. The first of these currencies were made of metals with lengthy shelf lives and low depreciation risks, such as gold, silver, and bronze.
Currency valuation is a contentious topic. Their fundamental physical qualities were initially what gave them worth. For instance, the price of extraction and some qualitative elements, including brilliance and purity content, determine the value of gold.
In the 17th century, the concept of a currency’s worth began to evolve. John Law, a well-known economist from Scotland, once stated that money, or currency issued by a government or king, “is not the value for which goods are exchanged, but the value by which they are exchanged.”
In other words, a currency’s value reflects its demand and capacity to promote both internal and external trade and business.
This line of reasoning is very similar to the current credit theory for monetary systems. According to this idea, commercial banks produce money (and the value of currencies) by making loans to borrowers. These borrowers then spend the borrowed funds on purchases, causing currencies to circulate in an economy.
Many worldwide currencies are now categorized as fiat after countries abandoned the gold standard in an effort to allay concerns about gold shortages. Governments issue fiat currency, which is not backed by any kind of asset but rather by people’s and governments’ trust in other people’s willingness to accept it.
Government-issued money today frequently takes the form of paper money, which lacks the inherent scarcity of precious metals. The amount of gold supporting paper currency controlled its worth for a very long time. Even today, there are still some currencies that are “representative,” meaning that each coin or note can be used to buy a certain quantity of a good.

The majority of the main currencies used today are fiat. Fiat currency has been discovered to be the most enduring and least prone to value loss over time by numerous governments and communities.
Fiat currencies’ value is determined by supply and demand. Because it is used by the largest economy in the world and controls the flow of payments in international trade, the U.S. dollar is seen as valued.
Bitcoin’s Value
The nature of bitcoin must be discussed in any discussion of its worth. Due to its physical characteristics, gold was a valuable currency, but it was also heavy. Although paper money was an advance, it still needs to be manufactured, stored, and is not as portable as digital currencies. Money has evolved digitally, moving away from physical qualities and toward more functional traits.
Here is one instance. Ben Bernanke, who was the Federal Reserve’s governor at the time and spoke on CBS’s 60 Minutes, recounted how the organization “rescued” insurance giant American International Group (AIG) and other financial companies from bankruptcy by providing money to them during the financial crisis. The interviewer was perplexed and inquired as to whether the Fed had created billions of dollars.
“So, to lend to a bank, we simply use the computer to mark up the size of the account that they have with the Fed,” said Bernanke. In other words, by making entries in its ledger, the Fed “manufactured” US dollars.
The capacity to “mark up” an account is an illustration of the characteristics of digital currencies. Because it streamlines and simplifies transactions involving currencies, it has ramifications for the velocity and use of such currencies.
Both a system of intermediary banks and the support of governmental agencies are absent from the bitcoin ecosystem. Bitcoin’s value is also seen in its network’s consensus-based transactions are approved by a decentralized network made up of different nodes. There is no government or other fiat authority to act as a counter party to risk and make lenders whole, so to speak, in the event that a transaction fails.
However, cryptocurrency does exhibit some characteristics of a fiat money system. It is rare and impossible to counterfeit. One could only carry out what is referred to as a double-spend in order to produce a fake bitcoin. When a user “spends” or transfers the same bitcoin in two or more different settings, they are essentially making a duplicate record.
The vastness of the Bitcoin network, however, makes double spending uncommon. It would be necessary to launch a so-called 51% attack, in which a small number of miners theoretically control more than half of the network’s power. This group might dominate the rest of the network to manipulate records by holding the majority of network power. A massive amount of time, resources, and processing power would be needed to launch such an attack against bitcoin, making it exceedingly implausible.
Fiat currencies are far less divisible than bitcoin. Up to eight decimal places can be used to split up a bitcoin into its component satoshis. For practical use, the majority of fiat currencies can only be divided into two decimal places.
Users with a minuscule fraction of a bitcoin will still be able to conduct transactions with the cryptocurrency even if bitcoin’s value keeps increasing over time. The creation of side channels like the Lightning Network may increase the economy’s worth even more.
Because of this rarity, bitcoin’s value is speculated to increase. The demand for cryptocurrencies has risen while the supply has shrunk. Investors are yearning for a piece of the profit pie that arises from trading its finite supply, which is growing ever larger.
Similar to gold, which has restricted uses that are mostly industrial, bitcoin similarly has limited utility. Blockchain, the technology that powers bitcoin, is being tested and used as a payment mechanism. Remittances across borders are one of its most efficient use cases for accelerating speed and reducing costs. Some nations, like El Salvador, are placing their bets on bitcoin’s value to advance to the point where it may be used as a medium for regular transactions worldwide.
According to another argument, the marginal cost of generating one bitcoin suggests that bitcoin’s value is indeed inherent.
It costs money for miners to mine bitcoins since it uses a lot of electricity. In a market when producers of the same good are competing with one another, the selling price of that good should converge to its marginal cost of production. According to empirical data, the cost of production tends to influence bitcoin’s value.
The supply of money, its velocity, and the value of the products generated in an economy are used by monetarists to try to calculate bitcoin’s value as they would money. The simplest method to go about it would be to estimate the value of bitcoin’s projected proportion by first examining the present global worth of all forms of payment and all other repositories of value that are comparable to bitcoin. Government-backed money is the most common form of exchange, thus for the purposes of our model, we shall only consider it. At the end of 2021, the money supply (M1) in the United States was, roughly speaking, worth more than $20 trillion.
If bitcoin’s value were to reach 15% of this valuation, its market capitalization in current dollars would be over $3 trillion, assuming that the total remained unchanged. That would put the cost of 1 bitcoin at about $143,000 with all 21 million bitcoins in circulation.
The main problem is that bitcoin is not a reliable store of value. The effectiveness of bitcoin as a medium of exchange determines how useful it is as a store of value. Bitcoin won’t be effective as a store of value if it fails to take off as a means of exchange.
Bitcoin’s value has been primarily driven by speculative interest for a large portion of its history. With sharp price increases and a media attention frenzy, bitcoin has shown signs of a bubble. Although the future is unpredictable, this is probably going to decrease as bitcoin continues to gain more general acceptance.
Bitcoin’s utility and transferability are also put to the test by challenges related to cryptocurrency storage and exchange platforms. Hacks, thefts, and fraud have plagued digital currency in recent years.
The market price of bitcoin is extremely erratic and prone to sharp price fluctuations. The market price at any particular time may therefore be greatly different from its true or inherent value. Nevertheless, overbought markets tend to cool off and oversold markets tend to recover over time. Without the advantage of hindsight, it is therefore impossible to determine whether bitcoin’s value is fair at one given moment.
Häufig gestellte Fragen - FAQ
Is Bitcoin a currency?
Despite the fact that bitcoin contains a number of characteristics of money, economists and authorities are still not persuaded that it is currently used as money. This is due to the fact that only a small number of transactions and items are priced in bitcoins. Despite the fact that users trade bitcoin frequently and move money throughout the network, there isn’t much business activity.
What Is the cost of Producing 1 BTC?
The price of electricity, mining difficulty, block reward, and miners’ energy efficiency all play a role in how much it costs to produce one bitcoin.
The price to produce 1 BTC is $26,529.30 with a block reward of 6.25 BTC, difficulty of 27.5 trillion, $0.15 per kWh, and energy efficiency of 45 joules per terahash.
Is Bitcoin backed by any physical asset or government?
No, bitcoin is not backed by any physical asset or government. Bitcoin’s value is primarily determined by the trust and adoption it receives from its users.
Can Bitcoin be compared to traditional currencies like the US dollar?
Bitcoin differs from traditional currencies in that it is not controlled by any central authority or government. Bitcoin’s value can be more volatile due to market sentiment and speculation.
Why does Bitcoin’s value seem so volatile?
Bitcoin’s price volatility is partly due to its relatively small market size compared to traditional assets like stocks or gold. Speculation, news events, and market sentiment also play a role in bitcoin’s value.









